Glycolysis
Glycolysis (also known as glycolytic pathway) is the metabolic process that releases energy from glucose. During glycolysis, a single molecule of glucose is split into two 3-carbon molecules, called pyruvates. At the same time, energy is extracted from glucose and converted into ATP, which is then used to fuel other cellular processes.
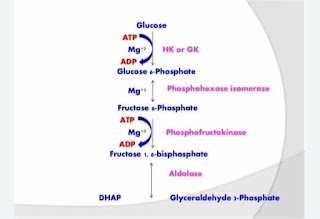
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of cells, can happen with or without oxygen, and involves a series of 10 chemical reactions
The 10 Steps of Glycolysis
There are 10 steps of glycolysis, each involving a different enzyme. Steps 1 – 5 make up the energy-requiring phase of glycolysis and use up two molecules of ATP. Steps 6 – 10 are the energy-releasing phase, which produces four molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADPH. The net products of glycolysis are two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules are ATP, and two molecules of NADPH.

0 Comments